Hemiarthroplasty
Hemiarthroplasty is a common surgery performed in the elderly to treat some fractures. ‘Hemi means half, and ‘arthroplasty’ means replacement. Hemiarthroplasty is the partial replacement of the hip joint. This surgery prevents the elderly from being bedridden and allows them to rehabilitate quickly.
Our Normal Hip Anatomy
The hip is a type of ball-and-socket joint. The socket is the acetabulum (part of the pelvis bone), and the ball is the femur head. The movement of this ball inside the socket is responsible for the movements of the hip, resulting in the leg going forward-backward, sideways, and rotating.
In a normal hip, the surfaces of the socket and the ball are covered with a tissue known as cartilage. The cartilage layer is responsible for painless and smooth joint movements. Damage or wear and tear of the cartilage leads to arthritis, which causes pain and restriction of joint movement.
In what conditions hemiarthroplasty is done?
Treatment in geriatric patients aims to mobilize them quickly and not make them bedridden for too long. It is mainly done in older people who have fractured necks or femurs. The surgery allows them to leave the bed and walk in 1-2 days.
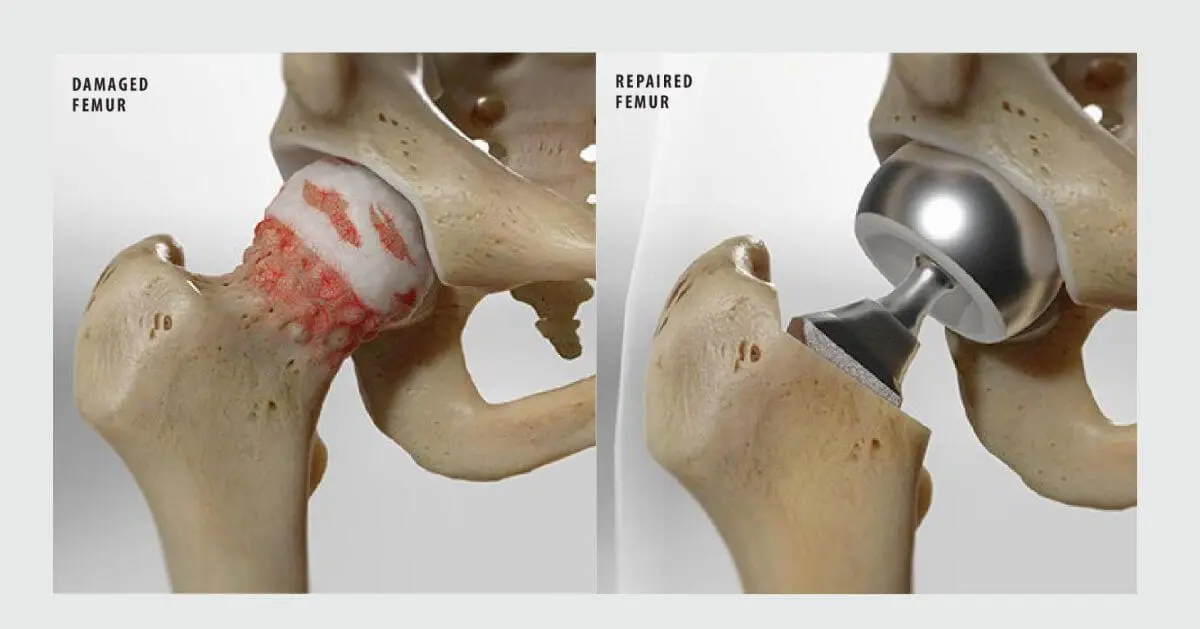
What are the components of hip replacement?
· The damaged/fractured femoral head is removed and replaced with a metal head. This new head is fixed with a metal stem in the femur (thigh bone). The metal stem can either be fixed using cement (Cemented hip replacement) or press-fit into the bone (Un-cemented Hip replacement).
What is the evaluation before surgery?
· History—Your doctor will ask how the patient got injured, how the patient was walking earlier, and what activities the patient could do.
· Physical examination – your hip will be examined for tenderness, strength, and the range of motion in your joint.
· Imaging – Radiographs will be taken of your joint to assess joint damage. Advanced imaging, such as CT or MRI, may be needed in some patients.
· Blood tests – Blood tests, ECG, and Chest X-ray are done before surgery to check the patient’s fitness. Sometimes, 2D-ECHO is also done in older patients. If you have any co-morbidities such as diabetes, hypertension, etc., they would need to be made under control before the surgery.
Realistic Expectations After Surgery
Most patients who undergo hemiarthroplasty experience a dramatic reduction in pain and improvement in their ability to perform their daily activities. Patients are allowed to walk, drive, bike, swim, play golf, and engage in other low-impact activities.
An artificial joint is prone to wear and tear like a typical joint. High-impact activities increase this process and, in turn, decrease the life of the implant. Therefore, patients are advised against high-impact activities such as jogging, running, jumping, etc.
Recovery at home after surgery
Wound care: You will have stitches or staples over your wound for a couple of weeks. There will be a dressing to seal the wound.
Diet: The patient may lose appetite for a few days after surgery. Eating a balanced diet is essential to healing the wound and good rehabilitation.
Activity: Basic exercises are taught to the patient during the hospital stay. The patient is also made comfortable walking with a walker. The patient must continue rehabilitation at home. Most patients can resume their daily activities within 3-6 weeks following surgery.