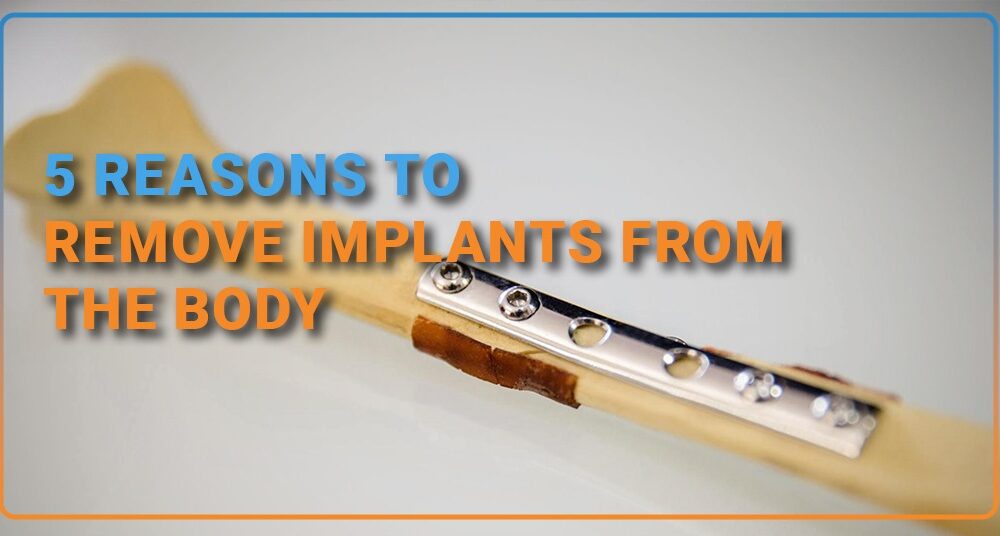
5 reasons to Remove Implants from the Body
Fractures often require metallic implants inside the body for fixation and treatment. The implants help in fracture union and can be in the form of wires, plates, screws, or rods. Is it mandatory to get them removed, or can we have them inside our bodies for a lifetime? What is the best time to get […]