If you have knee pain and difficulty doing even your daily activities, you may have severe arthritis. You may have Pain while doing daily activities such as sitting and walking.
If non-surgical treatments such as medicines, physiotherapy, and knee injections are no longer helpful, Total Knee Replacement is a perfect option for relieving knee pain.
When is Knee Replacement recommended?
There are many reasons why your doctor may recommend this surgery to you:
· Severe pain and stiffness Pain in your knees are affecting your daily activities. The patient may limp while walking and may even need to use support while walking.
· Pain in the knee Pain rests – while sitting and lying down.
· Deformities in the knees – bowing in or bowing out of the knees
· Failure of non-operative treatment (medicines, physiotherapy, intra-articular knee injections) to provide adequate relief.
Our Normal Knee Anatomy
Our knee is made up of three bones: the lower end of the femur (thigh bone), the upper end of the tibia (shin bone), and the patella (knee cap). The bone surfaces are covered with cartilage, which is responsible for smooth knee movements.
Two menisci are located inside the knee, between the tibia and femur. The menisci are C-shaped and present on the knee’s inner and outer compartments. These menisci act as shock absorbers and protect the knee from damage.
Many ligaments, namely the ACL, PCL, MCL, and LCL, keep the knee stable during movements.
The joint is covered with a synovial membrane, which releases synovial fluid. This fluid lubricates the cartilage and nourishes the ligaments and the menisci.
In what conditions is knee replacement done?
When the joint gets damaged, arthritic knee replacement is required.
1. Osteoarthritis: This is an age-related joint wear and tear. It occurs mostly in the elderly but is also seen in younger people. In this condition, the cartilage of the joint gets worn out, and the bones start rubbing each other during bending and movements. This wear and tear causes pain and stiffness in the knee.
2. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease in which the synovial membrane gets inflamed and starts damaging the joint cartilage. In long-standing and untreated diseases, the cartilage damage gets extensive, causing pain and complex knee movements.
3. Post-fracture: In fractures of the knee and around the knee, the knee cartilage gets damaged. Also, untreated meniscus and ligament injury cause further damage to the knee. Over time, these injuries cause further damage inside the knee, leading to pain and stiffness. What are the components of knee replacement?
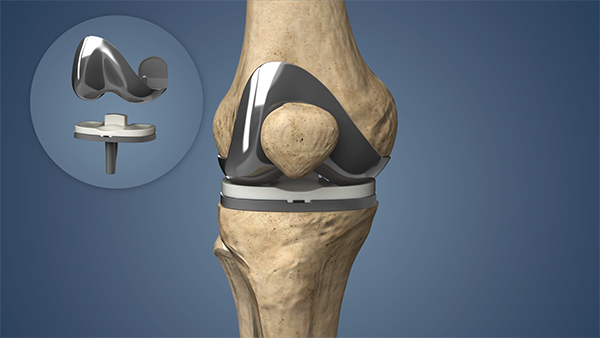
Also termed “Knee Surfacing” since only the surfaces of the bones are replaced. Knee replacement consists of 4 steps:
1. Bone Preparation: The damaged cartilage from the femur and the tibia are removed with a small area of underlying bone.
2. Implant Positioning: The removed cartilage and bone are replaced with metal implants over the bone surfaces. The implants can be fixed using cement or “press-fit” to the bone. The implants are inserted after sizing and trial so that the implant best suited to the patient’s knee is inserted.
3. Patella Resurfacing: In selected patients, the cartilage of the patella with some underlying bone is removed and replaced with a plastic button.
4. Spacer Insertion: A plastic (medical-grade) spacer is inserted between the tibia and femur components. This spacer creates a smooth, gliding surface for movements.
What is the evaluation before surgery?
· History – Your surgeon will take a detailed history regarding your condition. He will ask questions about your Pain and the problems you face daily.
· Physical examination – Your surgeon will examine your knee for pain improvements and deformity.
· Imaging – X-rays are done to check the damage in your knee. Advanced imaging, such as CT/MRI, may be required in a few patients.
· Blood tests – Blood tests, ECG, and Chest X-ray are done before surgery to check the patient’s fitness. Sometimes, 2D-ECHO is also done in older patients. If you have any co-morbidities such as diabetes, hypertension, etc., they would need to be made under control before the surgery.
Realistic Expectations After Surgery
Most patients who undergo hip replacement experience a dramatic reduction in pain and improvemPainin their ability to perform their daily activities. It is essential to understand what the procedure can and cannot do. The surgery will allow you to do those activities that you were able to do before you developed arthritis.
An artificial joint is prone to wear and tear like a typical joint. High-impact activities increase this process and, in turn, decrease the life of the implant. Therefore, patients are advised against high-impact activities such as jogging, running, jumping, etc.
Recovery at home after surgery
Wound care: You will have stitches or staples over your wound for a couple of weeks. There will be a dressing to seal the wound. You will need to follow the instructions given by your surgeon.
Diet: After the surgery, the patient may have decreased appetite for a few days due to the various medicines. Despite this, the patient should adopt a balanced diet, which will help in quicker rehabilitation.
Activity: You will be taught basic exercises, including walking, during your hospital stay. It is important that you continue those exercises at home. Most patients resume their daily activities 3-6 weeks after the surgery.